Temperature Control During the POY/FDY Process
Controlling the temperature during the POY (Partially Oriented Yarn) production process is crucial to ensure the desired quality and properties of the yarn. The specific temperature control methods can vary depending on the equipment and processes used, but here are some general guidelines:
Preheat the raw material: Before entering the extrusion process, the raw material, usually polyester chips, should be preheated to a specific temperature. This is typically done in a hopper or a preheating chamber. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the appropriate preheating temperature.
Extrusion process: The extrusion process involves melting the preheated polyester chips and extruding them through spinnerets to form filaments. To control the temperature during extrusion, consider the following:
a. Barrel temperature: The extruder barrel has multiple heating zones, each with its own temperature control. Adjust the temperature settings of these zones based on the specific requirements of the polyester chips being processed. Typically, the temperatures increase progressively from the feed zone to the metering zone.
b. Spinneret temperature: The spinneret, which contains the tiny holes through which the molten polyester is extruded, should be maintained at a specific temperature. This temperature is critical to achieve the desired filament diameter and properties. Consult the equipment manufacturer’s guidelines for the recommended spinneret temperature.
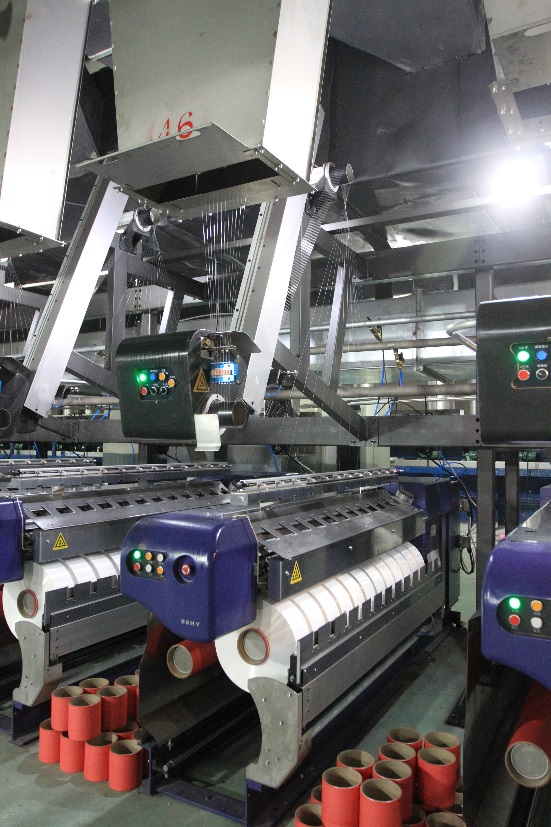
Quenching: After extrusion, the filaments are quenched to solidify them. This process typically involves passing the filaments through a cooling medium, such as air or water. The temperature of the quenching medium should be carefully controlled to ensure proper solidification and prevent any undesirable effects like filament sticking or deformations.
Drawing/stretching: Drawing or stretching the filaments is an important step in orienting the polymer chains and imparting desired properties to the yarn. During this process, the temperature needs to be controlled to achieve the desired level of orientation. Higher temperatures facilitate better stretching, but excessive temperatures can cause the filaments to degrade. The drawing temperature depends on the specific polymer being processed and its properties. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations or conduct trials to determine the optimal drawing temperature.
Annealing: Annealing is a heat treatment process performed on the stretched yarn to relieve internal stresses and improve its stability. The temperature and duration of annealing can vary based on the specific requirements of the yarn. Follow the recommended annealing parameters provided by the manufacturer or conduct trials to determine the optimal conditions.
Winding: During winding, the yarn is cooled further to ensure it maintains its shape and properties. The winding process may involve passing the yarn through a cooling chamber or using cool air or water jets. Control the temperature in this stage to prevent any heat-related issues or yarn deformations.
Remember, the specific temperature control parameters may vary based on the equipment and processes used in your POY production line. It is crucial to consult the equipment manufacturer’s guidelines, conduct trials, and optimize the temperature settings based on the desired yarn properties and quality requirements.